A.
STACK DENGAN SINGLE LINKED LIST
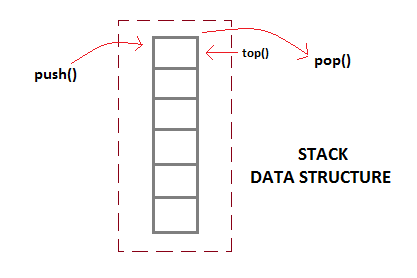
Stack daat diimplementasikan dengan single linked list.
Keunggulannya dibandingkan array adalah penggunaan alokasi memori yang dinamis
sehingga menghindari pemborosan memori.
Misalnya pada stack dengan array disediakan tempat untuk
stack berisi 150 elemen, sementara ketika dipakai oleh user stack hanya diisi
50 elemen, maka telah terjadi pemborosan memori untuk sisa 100 elemen, yang tak
terpakai. Dengan penggunaan linked list maka tempat yang disediakan akan sesuai
dengan banyaknya elemen yang mengisi stack.
Dalam stack dengan linked list tidak ada istilah full,
sebab biasanya program tidak menentukan jumlah elemen stack yang mungkin ada
(kecuali jika sudah dibatasi oleh pembuatnya). Namun demikian sebenarnya stack
ini pun memiliki batas kapasitas, yakni dibatasi oleh jumlah memori yang
tersedia.
Operasi-operasi
untuk Stack dengan Linked List
- IsEmpty
Fungsi memeriksa apakah stack yang adamasih kosong.
- Push
Fungsi memasukkan elemen baru ke dalam stack. Push di sini
mirip dengan insert dalam single linked list biasa.
- Pop
Fungsi ini mengeluarkan elemen teratas dari stack.
- Clear
Fungsi ini akan menghapus stack yang ada.
/*
* C Program to Implement a Stack using Linked List
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int info;
struct node *ptr;
}*top,*top1,*temp;
int topelement();
void push(int data);
void pop();
void empty();
void display();
void destroy();
void stack_count();
void create();
int count = 0;
void main()
{
int no, ch, e;
printf("\n 1 - Push");
printf("\n 2 - Pop");
printf("\n 3 - Top");
printf("\n 4 - Empty");
printf("\n 5 - Exit");
printf("\n 6 - Dipslay");
printf("\n 7 - Stack Count");
printf("\n 8 - Destroy stack");
create();
while (1)
{
printf("\n Enter choice : ");
scanf("%d", &ch);
switch (ch)
{
case 1:
printf("Enter data : ");
scanf("%d", &no);
push(no);
break;
case 2:
pop();
break;
case 3:
if (top == NULL)
printf("No elements in stack");
else
{
e = topelement();
printf("\n Top element : %d", e);
}
break;
case 4:
empty();
break;
case 5:
exit(0);
case 6:
display();
break;
case 7:
stack_count();
break;
case 8:
destroy();
break;
default :
printf(" Wrong choice, Please enter correct choice ");
break;
}
}
}
/* Create empty stack */
void create()
{
top = NULL;
}
/* Count stack elements */
void stack_count()
{
printf("\n No. of elements in stack : %d", count);
}
/* Push data into stack */
void push(int data)
{
if (top == NULL)
{
top =(struct node *)malloc(1*sizeof(struct node));
top->ptr = NULL;
top->info = data;
}
else
{
temp =(struct node *)malloc(1*sizeof(struct node));
temp->ptr = top;
temp->info = data;
top = temp;
}
count++;
}
/* Display stack elements */
void display()
{
top1 = top;
if (top1 == NULL)
{
printf("Stack is empty");
return;
}
while (top1 != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", top1->info);
top1 = top1->ptr;
}
}
/* Pop Operation on stack */
void pop()
{
top1 = top;
if (top1 == NULL)
{
printf("\n Error : Trying to pop from empty stack");
return;
}
else
top1 = top1->ptr;
printf("\n Popped value : %d", top->info);
free(top);
top = top1;
count--;
}
/* Return top element */
int topelement()
{
return(top->info);
}
/* Check if stack is empty or not */
void empty()
{
if (top == NULL)
printf("\n Stack is empty");
else
printf("\n Stack is not empty with %d elements", count);
}
/* Destroy entire stack */
void destroy()
{
top1 = top;
while (top1 != NULL)
{
top1 = top->ptr;
free(top);
top = top1;
top1 = top1->ptr;
}
free(top1);
top = NULL;
printf("\n All stack elements destroyed");
count = 0;
}
B. QUEUE DENGAN DOUBLE LINKED LIST
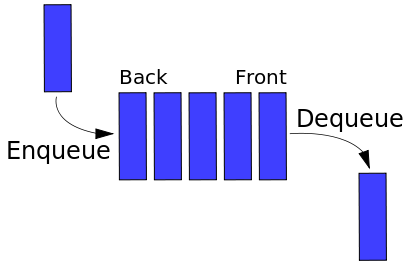
Selain
menggunakan array, queue juga dapat dibuat dengan linked list. Metode linked
list yang digunakan adalah double linked list.
Operasi-operasi
Queue dengan Double Linked List
- IsEmpty
Fungsi IsEmpty berguna untuk mengecek apakah queue masih
kosong atau sudah berisi data. Hal ini dilakukan dengan mengecek apakah head
masih menunjukkan pada Null atau tidak. Jika benar berarti queue masih kosong.
- IsFull
Fungsi IsFull berguna untuk mengecek apakah queue sudah
penuh atau masih bisa menampung data dengan cara mengecek apakah Jumlah Queue
sudah sama dengan MAX_QUEUE atau belum. Jika benar maka queue sudah penuh.
- EnQueue
Fungsi EnQueue berguna untuk memasukkan sebuah elemen ke
dalam queue (head dan tail mula-mula meunjukkan ke NULL).
- DeQueue
Procedure DeQueue berguna untuk mengambil sebuah elemen dari
queue. Hal ini dilakukan dengan cara menghapus satu simpul yang terletak paling
depan (head).
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <Windows.h>
struct antrian{
int value;
struct antrian *next, *prev;
}*head, *tail, *current;
void print(){
if(head!=NULL){
current=head;
while(current!=NULL){
printf("%d -> ", current->value);
current=current->next;
}
}else{
printf("No Data");
}
printf("\n\n");
};
void pushHead(int value){
current = (struct antrian *)malloc(sizeof antrian);
current->value=value;
current->next = current->prev = NULL;
if(head==NULL){
head=tail=current;
}else{
head->prev=current;
current->next=head;
head=current;
}
}
void popTail(){
if(tail==NULL){
printf("No Data");
}else if(tail==head){
current=tail;
head=tail=NULL;
free(current);
}else{
current=tail;
tail=tail->prev;
tail->next=NULL;
free(current);
}
}
void main(){
int menu;
int antrianke=1;
print();
do{
do{
system("cls");
print();
printf("1. Queue\n");
printf("2. DeQueue\n");
printf("3. Exit\n");
printf("Choose : "); scanf("%d", &menu); fflush(stdin);
}while(menu<1 || menu>3);
switch(menu){
case 1 :
pushHead(antrianke);
antrianke++;
break;
case 2 :
popTail();
break;
}
}while(menu!=3);
}
Comments
Post a Comment